Medical applications for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Deep Learning (DL) have drawn a lot of attention from investors, the media, and the public at large. Whether helping us better interpret radiological images, identify potentially harmful drug interactions, discover new therapeutic targets, or simply organize medical information, AI and DL are beginning to impact real care given to real patients. Because these systems learn from examining data, rather than being programmed to follow specific logic, it is often challenging to understand why they make the decisions they make. Furthermore, recent results suggest the role of AI in medicine is transitioning to a new phase, in which AI enables us to do more than merely solve known problems in an automated way. AI is enabling us to solve “xenocomplex” problems: problems so difficult, humans have a hard time identifying a solution or even fully articulating the problem itself. To fully translate these capabilities into better outcomes, we must recognize and come to terms with the ways in which AI may be able to solve problems we don’t fully understand.
Primer: What Is Deep Learning?
If you’re already familiar with AI and DL, this section will mostly be review. But if not, let’s begin with some background.
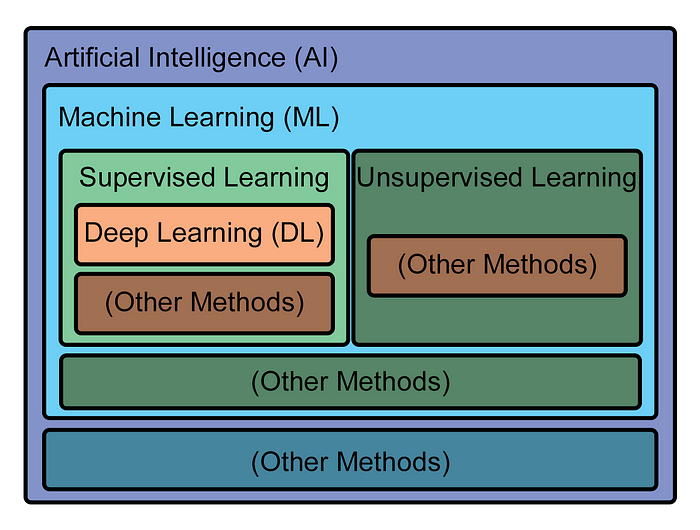
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broad term and simply refers to systems that (a) are non-human, and (b) display behavior that is “intelligent,” in that their behavior is a reasonable effort to pursue some goal. Machine Learning (ML) is a sub-domain of AI, which specifically refers to AI systems which “learn” how to pursue goals — how to appear intelligent — through examining data. Deep Learning (DL) is a further sub-domain of ML, in which learning is performed by a many-layered neural network examining multitudes of example datasets.
DL is a form of ML called Supervised Learning, which simply means that while the learning algorithm is being trained on its data, the data is labeled. The algorithm is told, for example, whether or not there is a cat in the picture it is examining, or is given a text transcript of an audio file. (As you might expect, another major form of ML, Unsupervised Learning, is when the algorithm doesn’t have labels for the data with which it is working.) Having a lot of well-labeled training data is a major factor in creating a well-performing supervised learning system, especially for DL systems.
Graphically, the hierarchy of methods looks like this:
Owing to their large body of well-labeled data, some of the greatest successes seen in DL have been in classic AI fields of study: image recognition, speech recognition, machine translation, natural language processing. In other classic areas, like playing chess or go, researchers devised clever means of training DL systems that essentially allowed the system to generate its own large, well-labeled training datasets.
Other than access to plenty of training data, these successes have another thing in common: they all are within domains humans understand well. Most people can easily tell if there is a cat in a picture or what words are in a speech (assuming they speak the language). People trained to do more difficult tasks can translate one language to another, play chess or go, or drive a car safely. Within their narrow domain, these AI’s are “doing things humans do,” but in an automated, often superior, way compared to humans.
Xenocomplexity and Challenging Domains
Neural networks are based on an idealized, simplified model of human neurons and neurological organs. While we can build powerful neural networks with ease, we often have difficulty pinning down why a neural network comes to a particular conclusion. When a neural network claims “there is a cat here” in a photo or translates “chez moi” to “my house,” we often can’t point at any specific chain of logic that led it to conclude that. We can easily tell if it got the answer right or not, but not why it got that answer. Neural networks suffer from a problem of inscrutability.
Their inscrutability arises because DL systems are not programmed to execute a specific problem-solving algorithm. They are programmed to learn and, even if data contain thousands or millions of interconnected variables, develop the ability to draw conclusions in complex, hyperdimensional space. This capability means a DL system can operate in a far more complex problem space than humans typically do. Neural networks have the potential to solve problems beyond human capacity. There is no reason DL systems must be confined to problems humans-solvable problems like identifying cats. In fact, there is no reason DL systems must be confined to solving problems humans can even articulate as problems in the first place.
For one example, DL systems have made significant progress on difficult problems in the field of chaos theory. Chaos theory is the formal study of chaotic systems; that is, systems whose development is extremely difficult to predict from their initial conditions. There are lots of examples of chaotic systems (remember Ian Malcolm with drops of water on his hand in Jurassic Park?). One problem chaos theorists use to develop and test new models is predicting the spread of a fire front. For several decades, researchers made steady, incremental progress using complex equations and ever-increasing computation to predict the evolution of a fire front. These equations consumed large numbers of connected variables and enabled them to predict the fire’s development a short time in the future, but the number and interconnectedness of their variables inevitably lead prediction to diverge from observation.
Then, in 2018, researchers at the University of Maryland employed a DL technique called reservoir computing to create a model that could predict eight times further into the future than all previous results. Importantly, their model had no human-coded knowledge about fire fronts or the complicated equations used to study them. All it had was a powerful learning model fed data generated by many fire front simulations, from which it learned to become good at predicting the behavior of future fire fronts given some initial conditions.
This result was a great achievement, and demonstrates a technique that may prove useful for making predictions in other chaotic systems, like the weather, heart arrhythmias, earthquakes, or supply chain disruptions. However, more fundamentally, it suggests another possibility: that humans are not intelligent enough to comprehend the true complexity of these systems. Perhaps the number of variables is too vast, or their connections are too nuanced, or the system is so complicated we are unable to reduce it to a system of rules we can grasp. Describing a system as “chaotic” may say more about our limitations as understanders of phenomena, rather than about the phenomena themselves. These phenomena can be described as xenocomplex: fundamentally too complex for humans to comprehend.
Xenocomplexity, AI, and Medicine
If we turn back to biology and medicine, we can see some inklings of problems which may exhibit xenocomplexity.
For example, in 2020, Google used a DL system called AlphaFold to achieve breakthrough results predicting protein structure, an extremely challenging though not formally chaotic problem. Like fire front growth prediction, the field of protein folding prediction had a long history, with a biennial competition for researchers to benchmark their algorithms against each other. Also like DL’s breakout predicting fire front development, AlphaFold’s 2020 blockbuster performance predicting protein structure dwarfed all previous approaches. Since that time, efforts by researchers and companies to exploit DL to design new proteins have exploded. AlphaFold’s dramatic success suggests it may be operating in a much more complex decision space than the best human minds were able to bring to bear, and that operating within this degree of complexity greatly improves the ability to successfully predict protein structure. These are aspects of a xenocomplex problem.
In another example, at Phase Genomics, our CytoTerra cytogenetics platformemploys DL to examine reams of structural data about the human genome to detect mutations implicated in cancer, infertility, and more. Due to a variety of factors, such as their small size, subtlety, complex rearrangement, cryptic nature, or presence in only a fraction of cells, many of these mutations are invisible to other techniques. Making sense of a complex phenotype related to these mutations, such as cancer or infertility, requires making sense of a large, complex body of genomic data and seems to confound human-authored logic. Hyperdimensional analysis models, like neural nets, seem far more successful at analyzing such data — another aspect of a xenocomplex problem.
Protein folding and interpreting genetic data may very well be xenocomplex problems, too challenging for humans to formulate and solve ourselves, and thus better suited to analysis by learning algorithms capable of operating in a more complex mathematical setting than us. It’s likely that as we continue to apply powerful AI methods to medicine, we will discover other xenocomplex problems. Xenocomplex medical problems deepen the question of how we will use AI in medical contexts: what if both the solution and the problem itself are inscrutable?
Should We Let AI Diagnose Xenocomplex Medical Issues?
There are a variety of possible answers to what we should do about xenocomplex problems in biology and medicine. In some cases, such as protein design, there is an easy answer: use DL to assist in designing the protein, make the protein, then test the protein. If the protein works, it’s not terribly relevant how it was designed. However, this becomes more challenging when resolving a xenocomplex problem itself delivers potential medical benefit. If an AI system predicts an otherwise healthy patient is at significant risk for heart failure, is it appropriate to treat them prophylactically? If an AI system claims a patient’s cancer is caused by a certain mutation requiring radical treatment, should that treatment begin?
The most common and comfortable answer to these kinds of questions, so far, has been that a doctor should review the results of any such AI-based test, and make the final recommendation. However, as AI continues to advance, it is inevitable that some systems will make diagnoses or recommendations based upon evidence that is not apparent or even understandable to a human physician. It’s likely that they will begin to detect and diagnose conditions that we do not know exist today, due to limitations in our ability to understand complex data. In such circumstances, a human reviewing results is at best a rubber stamp and at worst actively doing harm to the patient by second-guessing a system operating in a xenocomplex domain which they cannot comprehend. Including a human in the diagnostic process of a system like this would violate the physicians mandate to, first, do no harm.
Such a dilemma has been anticipated in numerous forms in science fiction. For example, in I, Robot, Isaac Asimov imagines how an extremely sophisticated AI might subtly guide humanity towards true happiness, even in defiance of what humanity might think would make it happier. In the Star Trek: TNG episode “Hero Worship,” Data rapidly consumes a large amount of information and concludes, in contradiction to what everyone else on the Enterprise believed, that the correct solution to a dangerous threat was to drop the shields rather than funnel all available power into them. Captain Picard, in that moment, trusted what his AI-powered officer recommended, even if he did not know why, and save the ship. As a human audience, we (and perhaps even the crew of the Enterprise) are finally treated to Data’s explanation that the threat was a harmonic power amplification, but one could easily imagine a similar situation in which Data understood a problem only perceptible with his vast computational abilities. When it comes to our healthcare, will we trust our AI-powered systems?
Of course, this is not to suggest AI-based systems should be thought of as infallible just because they operate on xenocomplex problems. However, it means that humans inserting themselves in the decision-making process for xenocomplex problems, at some point, on the balance, is detrimental. For every one incorrect decision they catch, for example, they might revert ten correct ones.
Medicine is by nature risk averse, and deciding what to do about these kinds of issues is not easy. Yet it’s an ethical question we as a society will have to address. Certainly, these kinds of tests will need to prove their accuracy and efficacy, like any other kind of diagnostic tool. At least for the foreseeable future, it will remain important for doctors and other appropriately trained medical staff to provide a sanity check on these methods. And yet, at some point, probably by the end of this decade and certainly by the end of the next, we will have to decide how we want to live with AI-powered diagnostic systems that understand us and our diseases better than we do ourselves. It is both exciting and a little frightening, but if we can embrace AI in medicine (with a dose of skepticism), the benefits to human health will be tremendous.
Comments